General Instructions for Creating Graphs and Figures
Examples below can be generated by plot_example.m or plot_example.py script in the Tools repository.
- It's recommended to place your figures reasonably;
prepare_figurefunction from the Tools can be used. - Do not forget to close your figures when not needed, e.g. close all figures at the beginning of your script.
| matlab | python |
|---|---|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # assumed in every code bellow |
|
close all | plt.close( 'all' ) |
- Each figure should a have descriptive title. Usually should be set after other drawing commands.
| matlab | python |
|---|---|
title( 'My title' ) | plt.title( 'My title' ) |
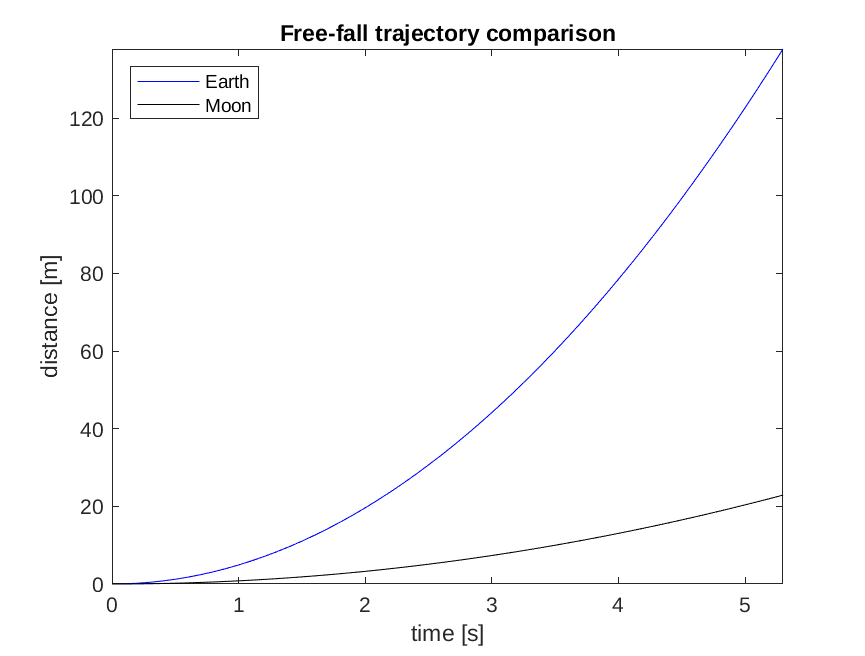
- When necessary, a legend describing lines of different colors/styles should be added, preferably inside the plot, if possible.
| matlab | python |
|---|---|
plot( …, 'DisplayName', 'Legend 1' ); | plt.plot( …, label='Legend 1' ) |
hold on | |
plot( …, 'DisplayName', 'Legend 2' ); | plt.plot( …, label='Legend 2' ) |
legend(); | plt.legend() |
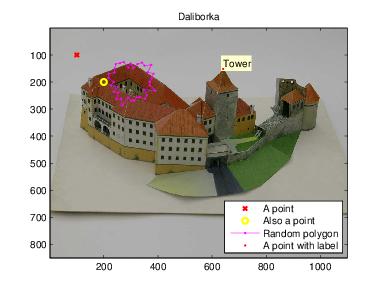
Figures with Bitmap Image Superimposed
- Show the image with axes.
- Ensure square pixels.
| matlab | python |
|---|---|
do not use imshow | |
image( rgb_img ) or imagesc( grayscale_img ) | plt.imshow( img ) |
axis image [*] or axis equal | plt.axis( 'image' ) [*] or plt.axis( 'equal' ) |
[*] This hides area outside the image.
2D Euclidean Plots
- Ensure isotropic axis scale
- Use labels for axes
- Use text descriptions when needed
| matlab | python | coment |
|---|---|---|
plot( x, y, … ) | plt.plot( x, y, … ) | |
axis equal | plt.axis( 'equal' ) | scale |
xlabel( 'x' ); | plt.xlabel( 'x' ) | labels |
ylabel( 'y' ); | plt.ylabel( 'y' ) |
|
text( x, y, '\alpha' ) | plt.plot( x, y, 'a' ) | text |
Note that Matlab can plot greek numbers using TeX sequences ( '\\alpha', '\\beta', etc.).
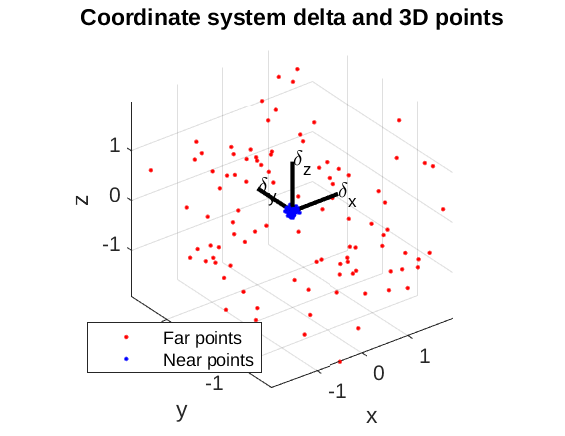
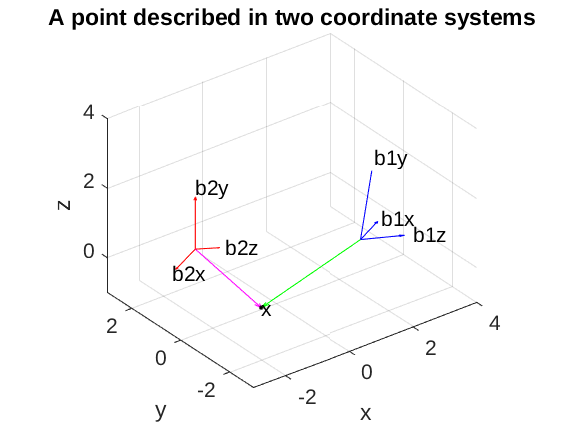
3D Euclidean Plots
- Same requirements as for 3D (scale, labels, …)
| matlab | python |
|---|---|
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d # 3D facilities, import before the .pyplot |
|
ax = plt.axes( projection='3d' ) # 3D axis must be explicitly created |
|
plot3( x, y, z, … ) | ax.plot3D( x, y, z, … ) |
text( x, y, z, … ) | ax.text3D( x, y, z, … ) |
axis( 'equal' ) | plt.axis( 'equal' ) |
zlabel( 'z' ); … | ax.set_zlabel( 'z' ) … |
Plotting vectors
- Bound vectors can be drawn using
quiver…functions. Origin (X,Y,Z) and vector coordinates (dX,dY,dZ) must be given.
| matlab | python |
|---|---|
quiver(X,Y,dX,dY,0) [*] | plt.quiver(X,Y,dX,dY) |
ax = plt.axes( projection='3d' ) |
|
quiver3(X,Y,Z,dX,dY,dZ,0) [*] | ax.quiver3D(X,Y,Z,dX,dY,dZ) |
[*] The scaling argument 0 ensures the arrow is of the proper length.